
Top Open Source Alternatives to Tonic AI for Data Anonymization and Synthetic Data
Top Open Source Alternatives to Tonic AI for Data Anonymization and Synthetic Data
March 31st, 2025

PlanetScale is a managed MYSQL database built on Vitess. It comes out of the box with branching, sharding, insights and more.
In this guide, we're going to walk through how you can seed your PlanetScale database with synthetic data for testing and rapid development using Neosync. Neosync is an open source synthetic data orchestration company that can create anonymized or synthetic data and sync it across all of your PlanetScale environments/branches for better security, privacy and development.
Let's jump in.
We're going to need a PlanetScale account and a Neosync account. If you don't already have those, we can get those here:
Now that we have our accounts, we can get this ball rolling. First, let's log into PlanetScale. If you already have a PlanetScale account then you can either create a new database or use an existing project. If you don't have a PlanetScale account then give your database a name, select a cluster size and create the database.
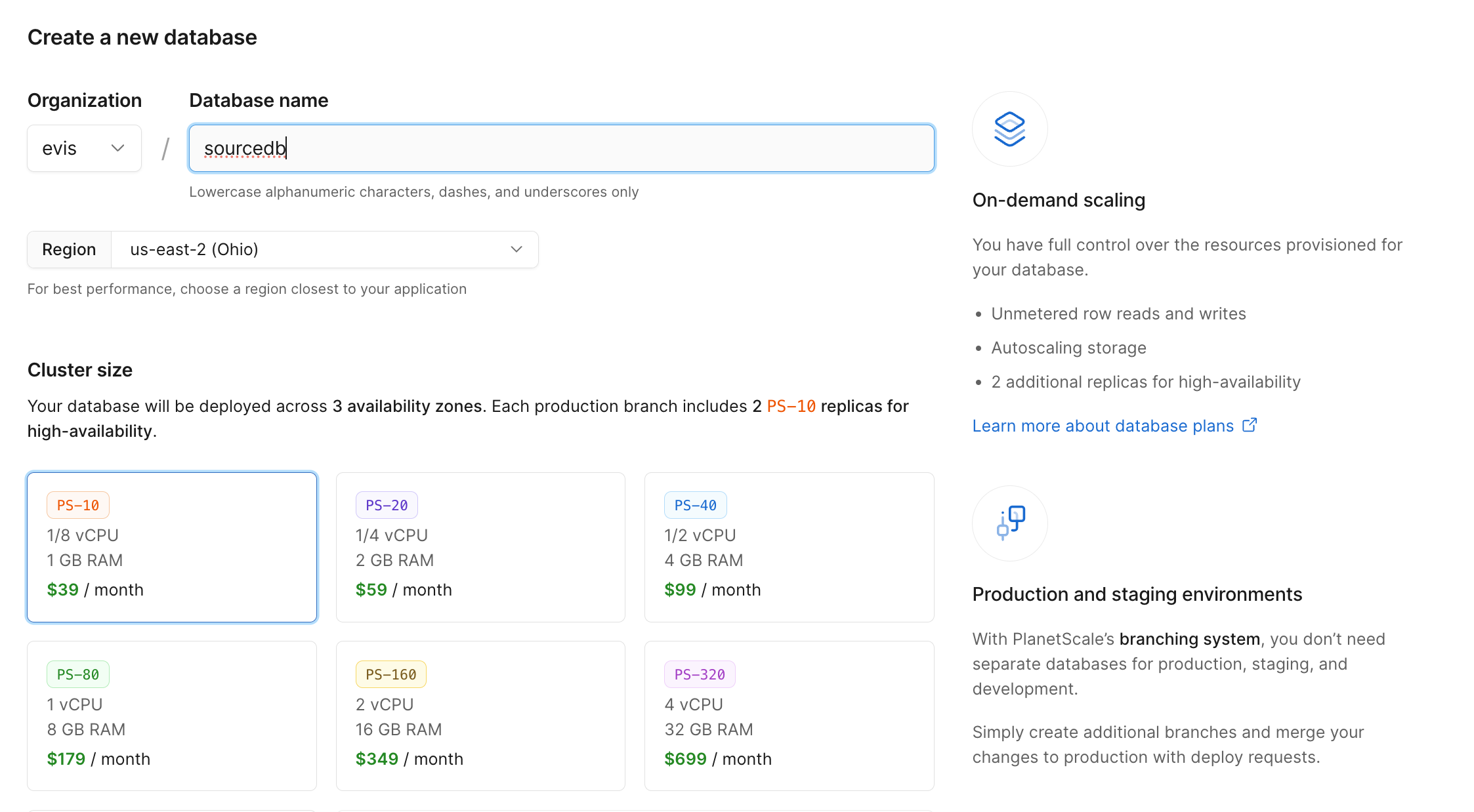
Now we can click on Create database in order to create our database.
PlanetScale will start to create your database. In the mean-time, you'll be asked tr create password and then select a language or framework to connect to your database. Click on 'I'll do this later' to skip this for now. We'll come back to it.
Once your database is created, you should see your dashboard look like this:
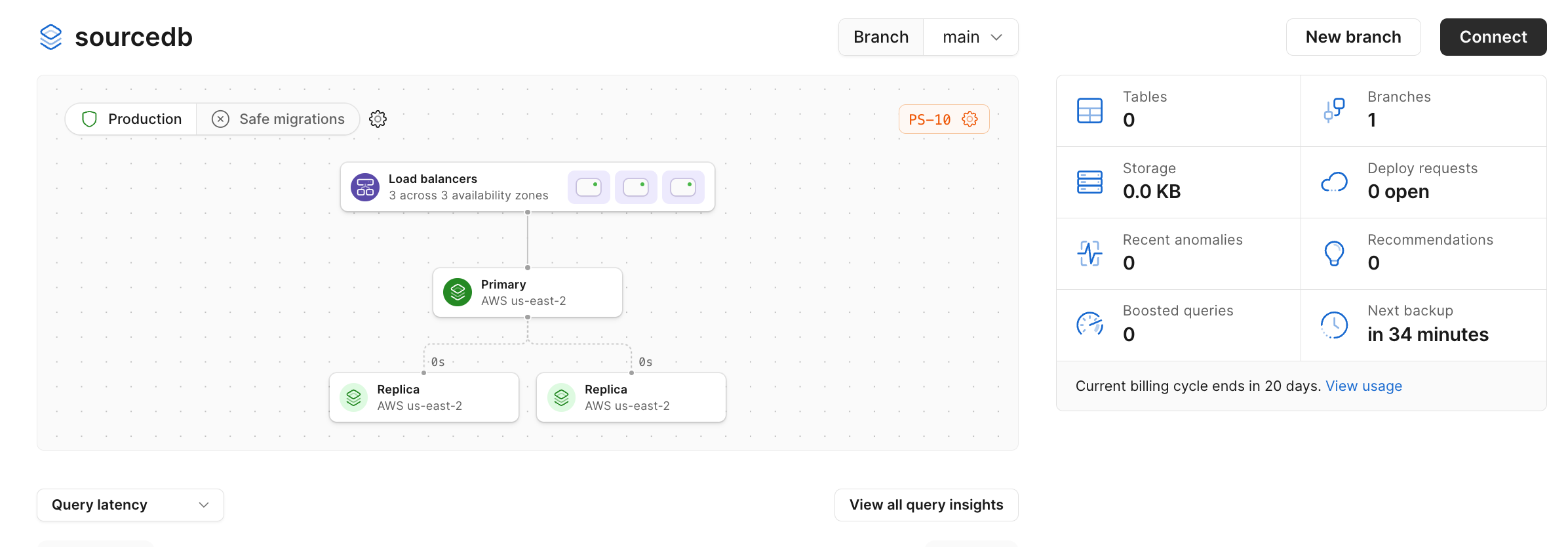
Next, we'll need to connect to our database and define our database schema.
Click on Connect on the top right hand corner and then make sure the connection type is 'Primary' and click Create Password. When you do that, a username and password will be created and displayed.
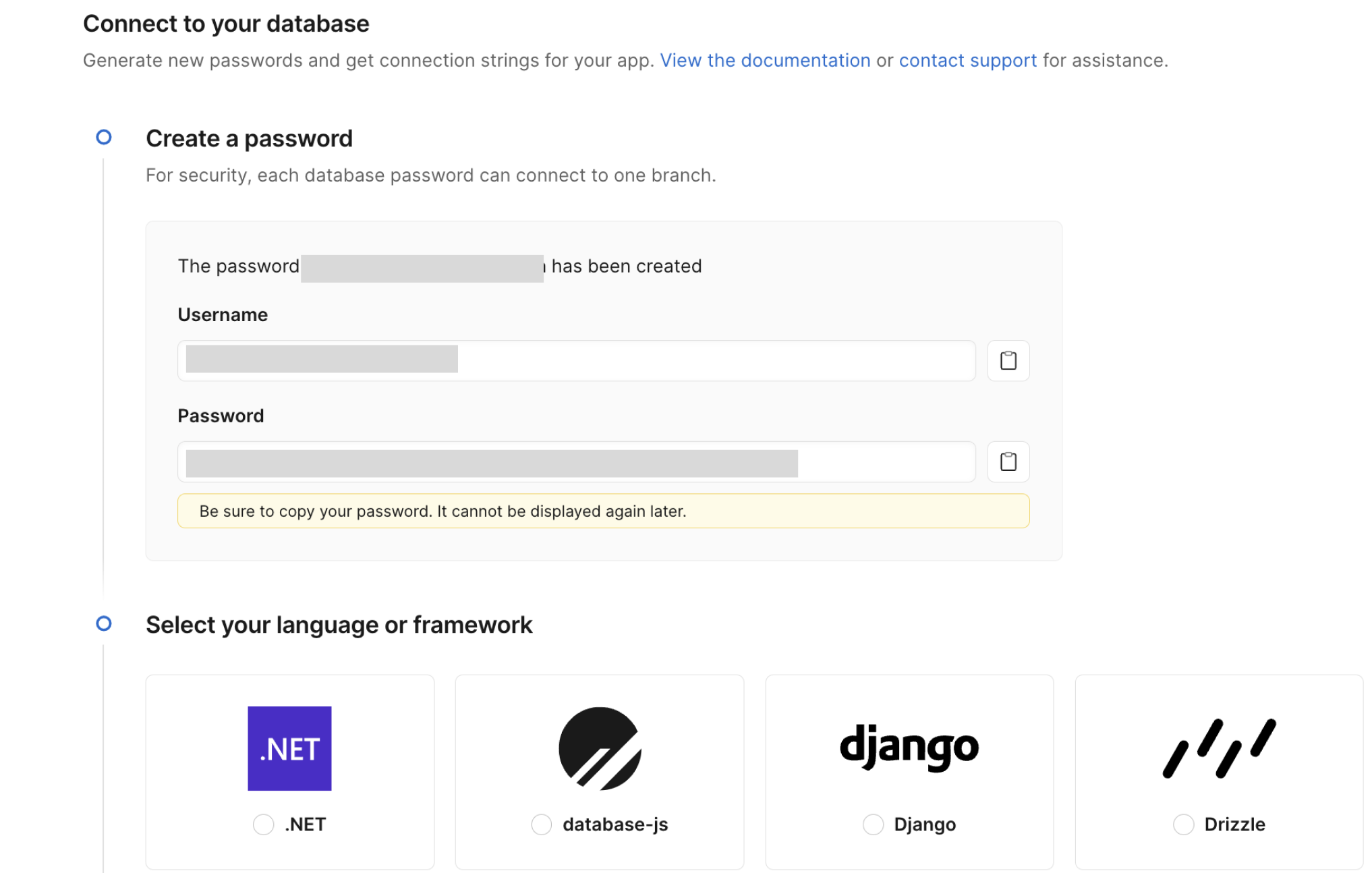
Scroll down to the language and framework section and select the last option, Other. Select the Optimized configuration and you'll see the Connection credentials section with your database params.
Connect to your database using your favorite client or the mysql CLI. Note: PlanetScale does have a web console but you'll need to create a new branch in order to access the web console as PlanetScale doesn't allow web console access to the main branch.
Once you're connected, here is the SQL script I ran to create our table:
CREATE TABLE users (
id CHAR(36) PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
age INT NOT NULL
);
We can do a quick sanity check on our database to make sure our columns are there.

Nice! Let's move to setting up Neosync.
Now that we're in Neosync, we'll want to first create a connection to our PlanetScale database and then create a job to generate data. Let's get started.
Navigate over to Neosync and login. Once you're logged in, go to to Connections -> New Connection then click on Mysql.
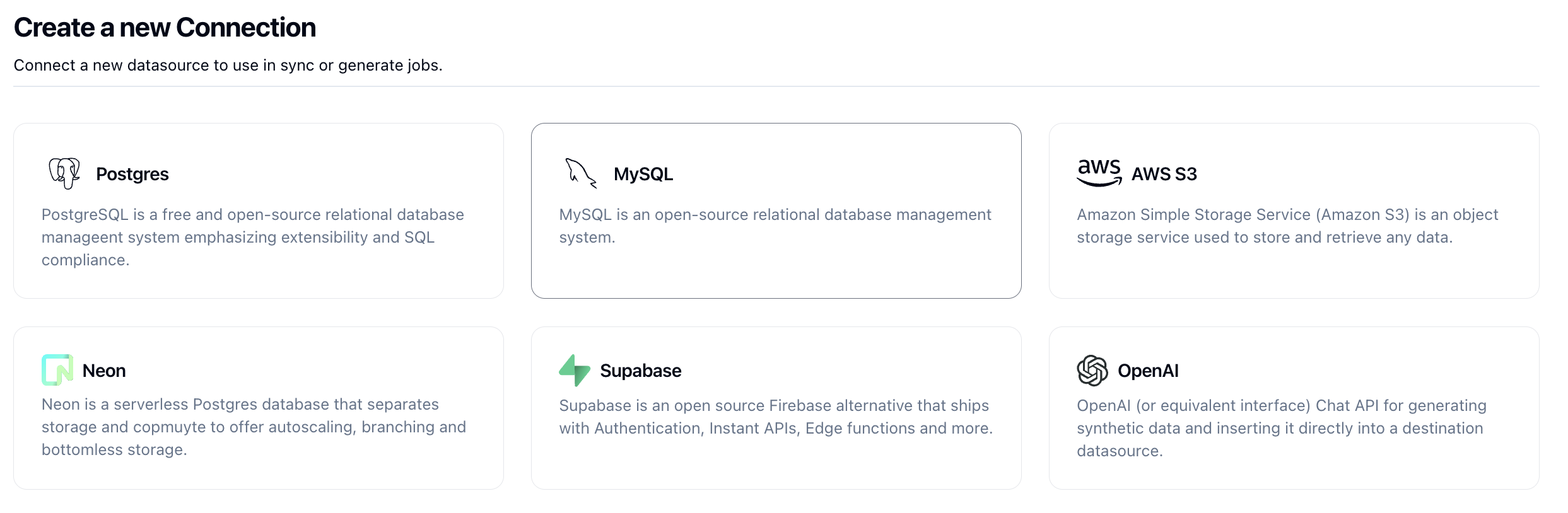
Let's use the Url tab to enter in our PlanetScale connection string to connect to our database.
This is the format for the connection string mysql://<username>:<password>@host:port/<database>?tls=true. Use the credentials from the PlanetScale dashboard to construct your connection string.
Once you've completed filling out the form, you can click on Test Connection to test that you're connected. You should see this if it passes:
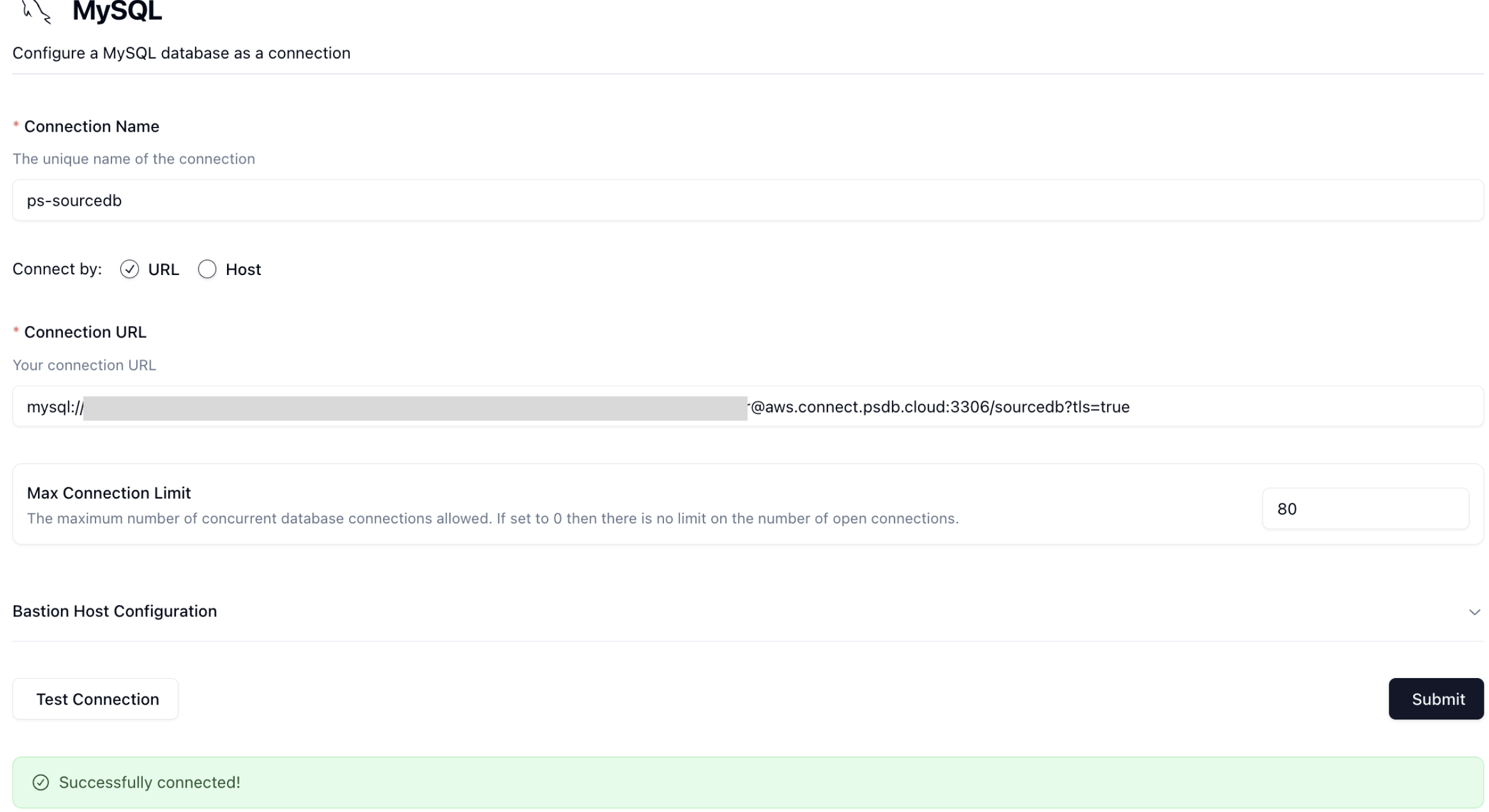
Let's click Submit and move onto the last part.
In order to generate data, we need to create a Job in Neosync. Let's click on Job and then click on New Job. We're now presented with three options:
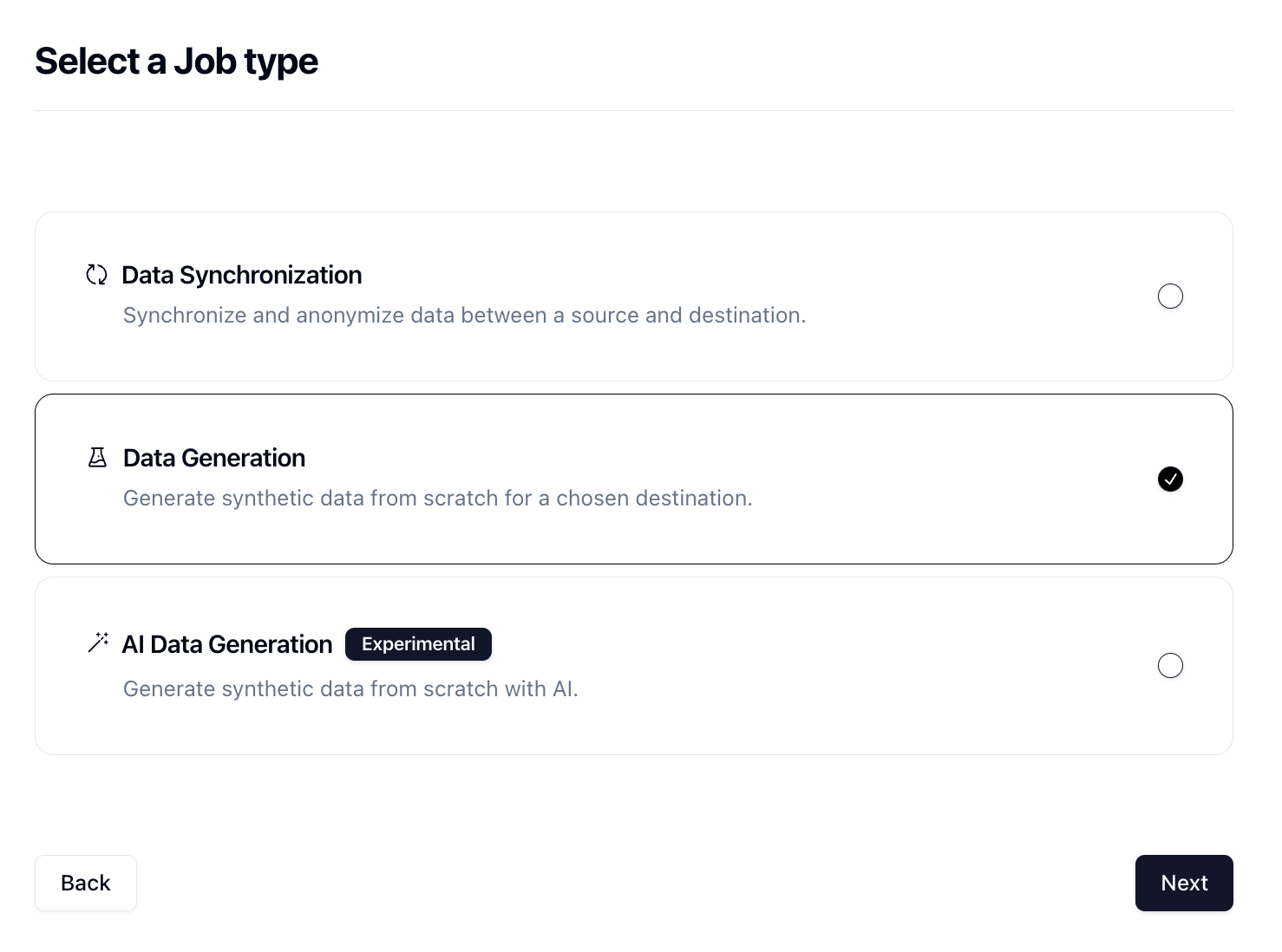
Since we're seeding a table from scratch, we can select the Data Generation job and click Next.
Let's give our job a name and then set Initiate Job Run to Yes. We can leave the schedule and advanced options alone for now.

Click Next to move onto the Connect page. Here we want to select the connection we previously connected from the dropdown.

There are some other options here that can be useful but we'll skip these for now and click Next.
Now for the fun part. First select your table. So I'm going to select the users table.
Next, decide how many rows you want to create. For this run, I'll do 10,000 rows.
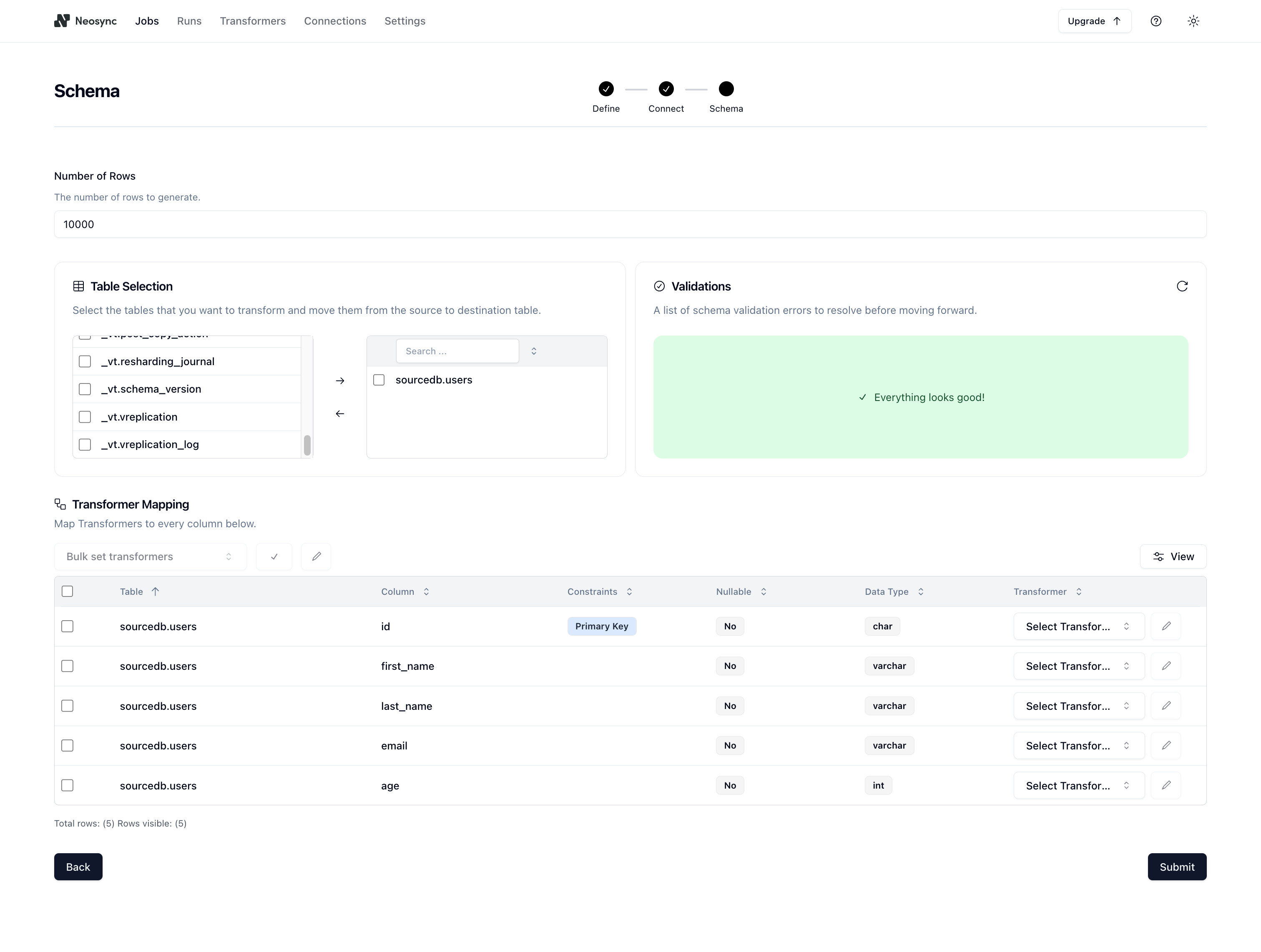
Lastly, we need to determine what kind of synthetic data we want to create and map that to our schema. Neosync has Transformers which are ways of creating synthetic data. Click on the Transformer and then select the right Transformer that maps to the right column. Here is what I have set up for the users table.
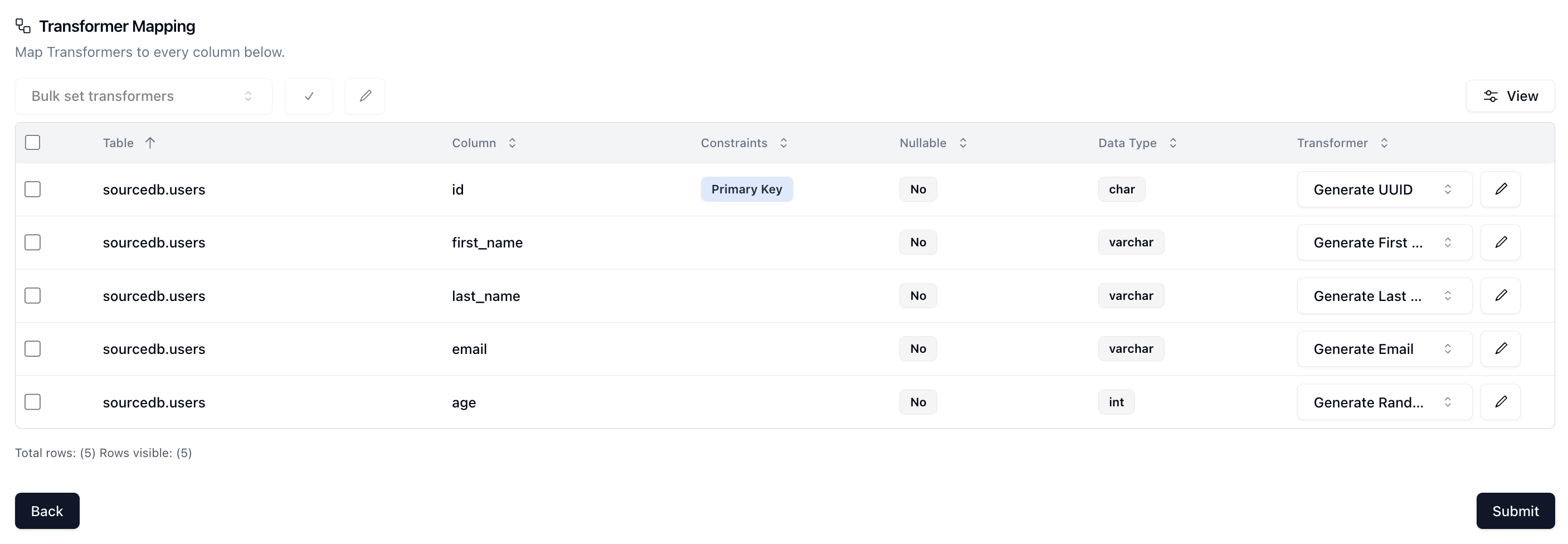
For the email column, I used the Generate Email Transformer to randomly generate email addresses and by clicking on the edit button I was able to set the email type to Full Name ensuring that the emails look like regular emails.
Now that we've configured everything, we can click on Next and create the job! We'll get routed to the Job page and see something like this:

You can see that our job ran successfully and generated 10,000 rows of synthetic data in just 1 second!
Now we can head back over to PlanetScale and check on our data. First let's check the count and make sure we generated 1000 rows.
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM users;
Next, let's check the data:
SELECT * FROM users;
Looking pretty good! We have seeded our PlanetScale database with 10,000 rows of completely synthetic data and it only took 1 second.
In this guide, we walked through how to seed your PlanetScale database with 10,000 rows of synthetic data using Neosync. This is just a small test and you can expand this to generate tens of thousands or more rows of data across any relational database. Neosync handles the referential integrity. This is particularly helpful if you're working on a new application and don't have data yet or want to augment your existing database with more data for performance testing.

Top Open Source Alternatives to Tonic AI for Data Anonymization and Synthetic Data
March 31st, 2025

Top 4 Alternatives to Tonic AI for Data Anonymization and Synthetic Data Generation
March 25th, 2025